Intermittent Fasting in today’s fast-paced lifestyle, health has become one of the most crucial priorities. People are constantly searching for effective ways to lose weight, boost energy, and stay fit. Among several diet trends and fitness strategies, intermittent fasting (IF) has gained immense popularity across the globe. It is not just a diet plan but a lifestyle pattern that focuses on when you eat rather than what you eat. From celebrities to fitness trainers and even medical professionals, intermittent fasting has become a widely recommended method for overall well-being.
This blog explores the concept of intermittent fasting, its benefits, methods, scientific background, and tips to follow it successfully.
What is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of fasting and eating. Unlike traditional diets that restrict certain food groups or calories, intermittent fasting emphasizes timing. The main principle is to give your body a prolonged break from digestion so that it can focus on repair, recovery, and fat-burning.
Historically, humans have practiced fasting for thousands of years, whether for religious, cultural, or survival reasons. In fact, our ancestors did not have access to food all day long, and their bodies adapted to eating in windows of time. Modern intermittent fasting draws inspiration from these natural eating rhythms.
Popular Methods of Intermittent Fasting
There are several approaches to intermittent fasting, and individuals can choose based on their lifestyle and goals:
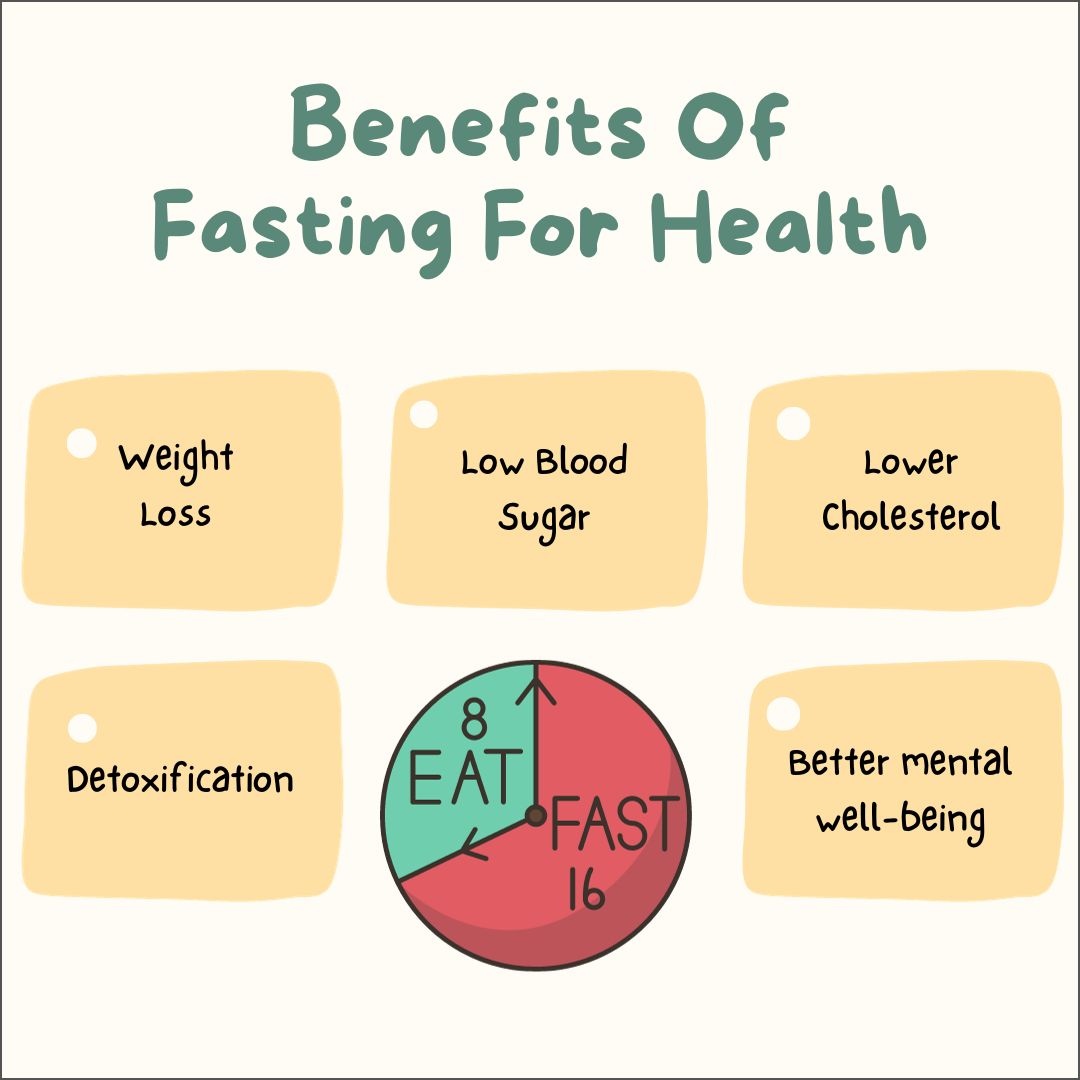
- The 16/8 Method
- The most common and easiest form of intermittent fasting.
- You fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window.
- For example, skip breakfast and eat between 12 PM to 8 PM.
- The 5:2 Diet
- Eat normally for five days of the week.
- Restrict calorie intake to 500–600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
- The Eat-Stop-Eat Method
- Involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week.
- Example: If you finish dinner at 7 PM, you do not eat until 7 PM the next day.
- The Warrior Diet
- Fasting for 20 hours with a small snack of fruits or vegetables.
- Eating one large meal at night within a 4-hour window.
- Alternate-Day Fasting
- Fasting every other day, either with zero calories or with a very limited intake.
Each method has its pros and cons, and the choice depends on your health condition, work schedule, and comfort level.
How Does Intermittent Fasting Work?
When you eat food, your body breaks it down into glucose (sugar), which becomes the main source of energy. The hormone insulin helps in transporting glucose into cells. However, when you are not eating (fasting), insulin levels drop, and the body starts using stored fat for energy.
This metabolic shift from glucose-burning to fat-burning is called metabolic switching. It not only helps in fat loss but also improves cellular repair and enhances overall metabolic health.
Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
1. Weight Loss and Fat Burning
Intermittent fasting naturally reduces calorie intake and increases fat burning. Studies suggest that IF can reduce belly fat, which is linked to various health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
2. Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Regular fasting lowers insulin levels and improves insulin sensitivity, making it effective in managing type 2 diabetes and reducing the risk of developing it.
3. Boosts Heart Health
Intermittent fasting can help reduce cholesterol, triglycerides, blood pressure, and inflammation – all of which contribute to better heart health.
4. Cellular Repair and Longevity
Fasting triggers autophagy, a process in which cells remove waste materials and repair themselves. This is believed to slow down aging and increase longevity.
5. Improves Brain Function
IF may support brain health by reducing oxidative stress, promoting the growth of new nerve cells, and lowering the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
6. Enhances Energy and Focus
Many people report improved mental clarity and stable energy levels after adapting to intermittent fasting. This happens due to stable blood sugar levels and better fat utilization.
Challenges and Side Effects
While intermittent fasting offers many benefits, it may not be suitable for everyone. Some common challenges include:
- Hunger and cravings during the initial phase.
- Headaches, irritability, or weakness as the body adapts.
- Overeating during the eating window, which can reverse the benefits.
- Not recommended for pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, underweight individuals, or those with certain medical conditions unless guided by a doctor.
With patience and gradual adaptation, most people overcome these difficulties.
Tips to Succeed with Intermittent Fasting
- Start Slow – If 16 hours seems tough, begin with 12 hours and gradually increase.
- Stay Hydrated – Drink plenty of water, herbal teas, or black coffee during fasting.
- Eat Nutritious Meals – Focus on whole foods, lean proteins, vegetables, healthy fats, and whole grains.
- Avoid Junk Foods – Eating unhealthy processed foods during your eating window defeats the purpose.
- Stay Busy – Keep yourself engaged to avoid thinking about food.
- Listen to Your Body – If fasting makes you extremely weak or sick, stop immediately.
- Combine with Exercise – Light workouts during fasting periods can accelerate fat burning.
Intermittent Fasting and Lifestyle
Intermittent fasting is not just about weight loss. It can transform your overall lifestyle. By simplifying meal planning, reducing snacking, and helping you eat more mindfully, it encourages discipline and better control over your eating habits. It also frees up time that would otherwise be spent cooking or eating multiple meals.
Moreover, intermittent fasting has cultural and spiritual significance. Fasting has been a part of traditions like Ramadan, Navratri, and Lent, proving that humans can thrive without constant eating.
Conclusion
Intermittent fasting is more than a fitness trend – it is a lifestyle shift with powerful benefits for body, mind, and health. By aligning with our natural biological rhythm, it helps in fat loss, boosts metabolism, enhances brain function, and even promotes longevity. While it may not be suitable for everyone, most healthy adults can adapt to it with patience and discipline.
If practiced mindfully with a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, intermittent fasting can be a simple yet effective key to long-term well-being